Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Prostate Health Archive
Articles
Treatment versus monitoring of prostate cancer: Survival rates the same after 10 years
Two new studies add to the evidence that for many men with prostate cancer, if it is detected early and has not metastasized beyond the prostate gland, monitoring the cancer will lead to the same chance of survival after 10 as choosing surgery or radiation. Men treated with surgery or radiation often experience significant side effects. The rates of depression and anxiety were the same in men who opted for monitoring and those who opted for treatment.
Treatment versus monitoring of prostate cancer: Survival rates the same after 10 years
Charles Schmidt A pair of new studies provides useful information to men facing challenging decisions about what to do after being diagnosed with early prostate cancer. Researchers tracked men for 10 years and found that virtually none died of the illness, even if they decided against treating it. Early prostate tumors confined to the prostate […]
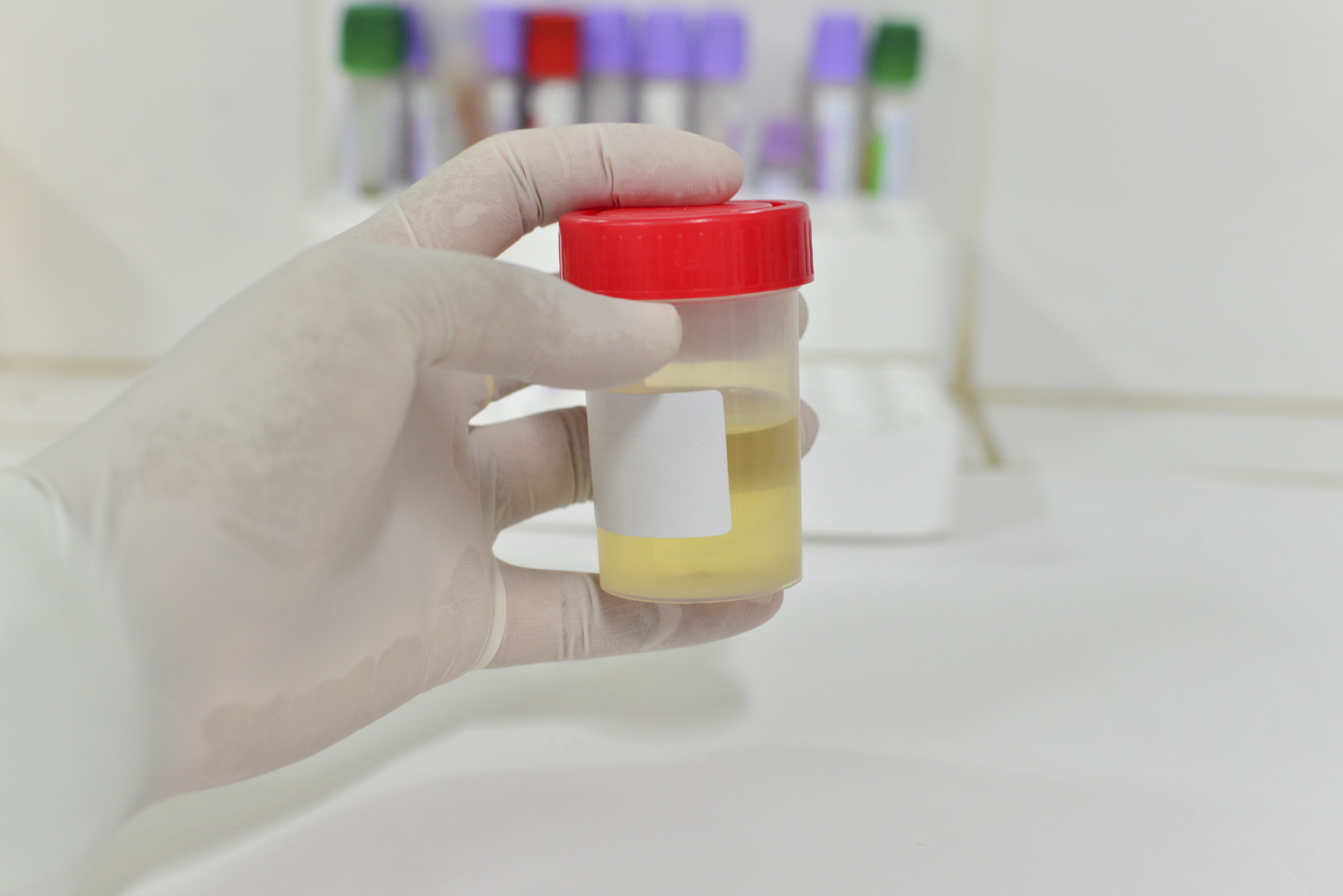
New urine test predicts high-grade prostate cancer
Researchers believe that a non-invasive screening test that can identify genetic markers for high-grade prostate cancer in urine may eventually reduce the number of prostate biopsies needed. However, experts also caution that while the number of non-invasive tests for prostate cancer diagnosis is growing, these are still early days in their development.
The risks of active surveillance for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancers
Many men with prostate cancer benefit from active surveillance, in which treatment doesn’t begin unless the cancer spreads. There has been some debate about whether this strategy is safe for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer. A new study suggests that this type of cancer is more likely to spread than previously thought �� but active surveillance can still be a good option for many intermediate-risk men.
Risks of active surveillance for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancers
Men diagnosed with slow-growing prostate tumors that likely won’t be harmful during their lifetimes can often avoid immediate treatment. Instead, they can have their tumor monitored using a strategy called active surveillance. With this approach, doctors perform periodic checks for tumor progression and start treatment only if the cancer begins to metastasize, or spread. Active […]
Active surveillance is safe for low-risk prostate cancers
A new study confirms that active surveillance is a safe and reasonable alternative to immediate treatment for prostate cancer. In recently published study that followed 1,300 men, the prostate cancer survival rate after 10-15 years of active surveillance, was 99%. For some men, a strong discomfort with “living with cancer�� may steer them away from postponing treatment in favor of careful monitoring.

Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up