Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Medical Tests & Procedures Archive
Articles
When should I be concerned about the color of my urine?
On call
Q. When should I worry about changes in the color of my urine? What color is considered healthy?
A. If a person is well hydrated, the normal color of urine is a pale yellow. Someone who drinks large amounts of fluid or takes diuretics (water pills) can have almost clear-looking urine. A dark yellow color may indicate a need to increase your fluid intake.
Hepatitis C screenings now include all adults up to age 79
��
News briefs
The guidelines are changing when it comes to screening for hepatitis C, a silent viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause cirrhosis, liver cancer, or liver failure. Back in 2012, the CDC recommended a one-time hepatitis C screening for the so-called baby boomer generation (anyone born between 1945 and 1965), a group that made up about 75% of all hepatitis C cases at that time. The following year, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) agreed. Now the USPSTF is expanding the screening age to all adults ages 18 to 79. The move is meant to identify more people in early stages of infection and comes as hepatitis C cases have increased almost fourfold since 2010. The USPSTF also advises screening for people outside of the recommended age range if they have ever used injected drugs. The recommendations were published online March 2, 2020, by JAMA. The CDC is in the process of developing similar recommendations. The screening requires only a simple blood test.
Image: jarun011/Getty Images
Testing for dementia
If you or someone else suspects early signs of memory loss, here's how you can find out if there's a problem.
There's no cure for dementia, and you cannot substantially reverse its effects, but there are ways to possibly slow its progression. But first, you need to know if you �� or a loved one �� may have a memory disorder. "Unfortunately, there is not one single test that confirms dementia while you are alive," says Dr. Julie Brody Magid, clinical director of the Harvard-affiliated McLean Hospital Memory Disorders Assessment Clinic. "The testing process is multilayered and takes many things into consideration. Going through this evaluation may help identify memory problems before they get worse."
Know the symptoms
Symptoms of dementia include memory loss, problem-solving difficulties, and language issues. Behavior and emotions also can be affected. Symptoms are often subtle early on, and then get progressively worse. They can increasingly interfere with daily life tasks, like remembering to attend appointments, take medication, or pay bills. People also may have trouble preparing meals or driving safely.
Heart tests before surgery: When are they necessary?
Most people don't need an electrocardiogram before a minor, low-risk procedure. Major surgery is different.
If you've ever had surgery, you may recall having a preoperative evaluation, sometimes referred to as "clearance" for surgery. These check-ups often occur days or weeks prior to a planned, non-cardiac surgery and typically involve a physical exam. You also may get blood tests, x-rays, and an electrocardiogram (ECG) �� a quick, painless test that records your heart's electrical activity.
"These evaluations are designed to assess your chances of experiencing a heart-related problem during the surgery," says Dr. Brendan Everett, director of the general cardiology inpatient service at Harvard-affiliated Brigham and Women's Hospital. The term "clearance" is misleading, as there is no way to guarantee you won't have complications. Still, knowing ahead of time about any heart-related risks you may have enables the surgeon to better prepare for possible complications and have a backup plan available, says Dr. Everett.
Clearing clogged arteries in the neck
Balloon angioplasty appears to be just as good as surgery to unblock carotid arteries.
Date of last review, March 25, 2020Opening a blocked heart artery with a balloon and then propping it open with a wire-mesh stent is more commonly used than bypass surgery for restoring blood flow to the heart. Although coronary angioplasty plus stenting isn't quite as durable as bypass surgery, it is much easier on the body, since it doesn't require opening the chest.
The situation is similar in the carotid arteries, which convey oxygen-rich blood to the brain. In that territory, carotid angioplasty plus stenting (CAS) for many people has become preferred to endarterectomy, an operation to clean out a clogged carotid artery.
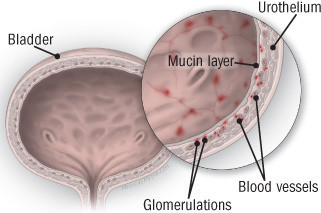
Diagnosing and treating interstitial cystitis
Also called painful bladder syndrome, this frustrating disorder disproportionately affects women.
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic bladder condition that causes recurring bouts of pain and pressure in the bladder and pelvic area, often accompanied by an urgent and frequent need to urinate �� sometimes as often as 40, 50, or 60 times a day, around the clock. Discomfort associated with interstitial cystitis can be so excruciating that, according to surveys, only about half of people with the disorder work full-time. Because symptoms are so variable, experts today describe interstitial cystitis as a member of a group of disorders collectively referred to as interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. (In this article, we'll call it interstitial cystitis, or IC.)
Among the one to two million Americans with IC, women outnumber men by as much as eight to one, and most are diagnosed in their early 40s. Several other disorders are associated with IC, including allergies, migraine, irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia (a condition causing muscle pain), chronic fatigue syndrome, and vulvodynia (pain or burning in the vulvar area that isn't caused by infection or skin disease).
Biotin supplements may interfere with test to diagnose heart attack
Research we're watching
Taking supplements that contain high levels of biotin (vitamin B7) can lead to falsely low results on a blood test used to detect heart attacks, according to an FDA warning issued late last year.
For adults, the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for biotin is 0.03 milligrams (mg), which is easily obtained through a healthy, varied diet. Many multivitamins and prenatal vitamins contain far more biotin than the RDA. And some supplements �� particularly those marketed to improve hair, nails, and skin �� contain 20 mg, or nearly 650 times the RDA.
Is there an age limit for a colonoscopy?
On call
Q. I'm 80 and no longer do colon cancer screening. However, I recently noticed some bleeding from my rectum. Does that change my need for a colonoscopy?
A. Screening for a disease means the person has no symptoms. Since you now have rectal bleeding, a colonoscopy would be considered not a screening test, but a diagnostic test. Whether you have it now or wait to see if more bleeding occurs depends upon many factors. The most important question is whether anything found on the colonoscopy will lead to treatment that improves your quality of life.
2020 vision: Cardiology trends to watch
Several new technologies and medications that may benefit the heart are moving into cardiology care.
As regular readers of the Heart Letter know, our features tend to focus on lifestyle advice and currently available therapies for heart disease. As the new decade begins, we're also looking to the future. Editor in Chief Dr. Deepak L. Bhatt selected five promising new developments in cardiovascular research that you may be hearing more about in the coming years.
1. Digital stethoscopes
First developed more than 200 years ago, the instrument doctors use to listen to the heart and lungs has undergone some high-tech improvements in recent years. The latest digital stethoscopes feature specialized microphones and sensors that filter, buffer, and amplify sounds from the heart. The sounds are then converted to a digital signal and sent wirelessly to a smartphone, where the patterns can be visualized and further analyzed. Some models are so sensitive they can detect turbulent blood flow in the arteries of the heart, possibly enabling doctors to detect coronary artery disease. Studies assessing that potential use are currently under way.
What to do about incidental findings
They often lead to follow-up appointments and more testing.
Modern medical imaging saves lives: it can find a blocked artery, a bulging blood vessel, or a suspicious mass. But many times, an x-ray, CT scan, MRI scan, or ultrasound exam looking for one kind of problem can reveal an anomaly that's unrelated and unexpected. Such incidental findings can lead to more testing, more medical bills, and a great deal of anxiety.
"Frequently radiologists will point out something and say it's probably benign, but recommend an MRI. Once you've been told something might be abnormal, you might feel nervous until you know what it is," says Dr. Suzanne Salamon, associate chief of gerontology at Harvard-affiliated Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.

Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up