Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Digestive Health Archive
Articles
Feed your gut
Some fermented foods contain probiotics, beneficial microorganisms that can live in your intestines. These microorganisms help you stay healthy, potentially improving your immune function and reducing damaging inflammation. Eating prebiotics—high-fiber foods that are a source of nutrition for these healthful microorganisms—is essential to help these beneficial microorganisms grow and thrive.
IBS in the crosshairs
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) affects up to 45 million Americans, two-thirds of whom are women. IBS is categorized into three types depending on which symptoms dominate: diarrhea, constipation, or a mix of both. Possible contributors include changes in gut bacteria, faulty nerve signals between brain and intestine, pelvic floor problems, and genetics. Newer treatment approaches target pathways involved in symptoms. Doctors are also repurposing older drugs for IBS, including certain antidepressants and the antibiotic rifaximin (Xifaxan).
Do our microbes affect our behavior?
Scientists wonder if gut microbes might influence behavior in animals, including humans. Some studies suggest a link. For example, a 2022 study suggested that gut microbes can influence an animal's motivation to exercise. Scientists speculate that the same might be true in humans. Other studies have found that a parasite called Toxoplasma gondii is tied to risky behavior in lab mice and risk-taking behaviors in humans. Scientists now even consider it conceivable that gut microbes might influence things like human intelligence, attitudes, empathy, and more, although the idea has yet to be proved.
Was it something you ate? Follow these steps when food makes you sick
Symptoms of food-related illness can show up hours or even days after ingesting a harmful microbe or toxin. Symptoms of food-related illness might include intense nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, diarrhea, or possibly a low-grade fever (below 101° F). Someone with food-related illness should rest as much as possible, stay hydrated, and avoid sugary drinks or alcohol. A person who develops a high fever, bloody stool, severe abdominal pain, or severe dehydration should go to the emergency room.
Can long COVID affect the gut?
Some people who have been infected with the virus that causes COVID-19 have experienced lingering effects like low energy and brain fog. Could gastrointestinal problems be another aftereffect of the virus?
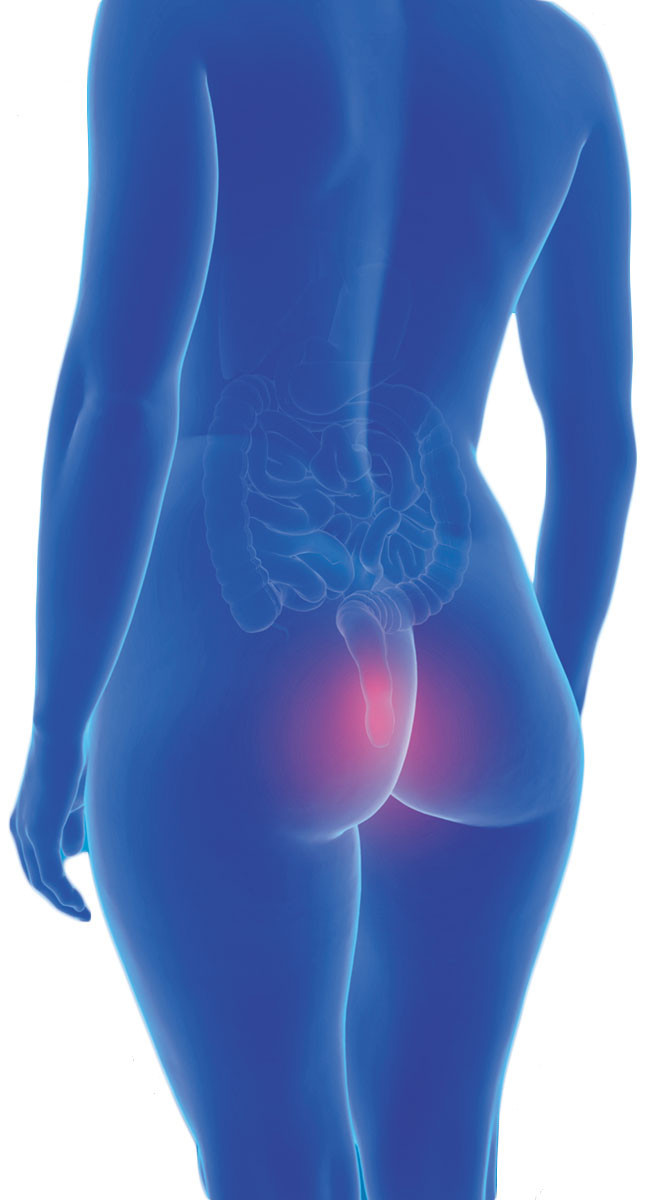
A pain in the rear
Everyone is born with the blood vessels that underlie hemorrhoids, but they may become problematic when they enlarge. Half of people have symptoms by age 50 that include pain, itching, swelling, and bleeding. Home remedies such as pain relievers, topical creams and ointments, sitz baths, and cold compresses don't eradicate hemorrhoids. In-office procedures can cut off blood supply to internal hemorrhoids, allowing them to fall off. Surgery is the only definitive treatment option for external hemorrhoids visible at the anus.
Healthy gut, healthy heart
The gut is home to trillions of microbes, collectively known as the gut microbiota, which help with digestion, manufacture certain nutrients, and release various substances that have wide-ranging health effects, including on cardiovascular health. As diet plays a significant role in the composition of the gut microbiota, people's diet can indirectly affect heart health. Following a plant-based diet that emphasizes less red meat and more fiber can support the gut and its heart-healthy benefits.
You don't say? Facts about flatulence
It's normal to accumulate and release gas; in fact, the average person releases two liters of gas per day. Certain foods can increase gas production since they take longer to digest.
Prune juice for constipation? A new study says yes
Drinking about one cup of prune juice daily may help relieve chronic constipation, according to a 2022 study.

Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up