Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Cancer Archive
Articles
Cancer and diet: What’s the connection?
Your dietary habits can promote cancer or protect against it.
��Image: Udra/ Thinkstock
The link between cancer and diet is just as mysterious as the disease itself. Much research has pointed toward certain foods and nutrients that may help prevent—or, conversely, contribute to—certain types of cancer.
While there are many factors you can't change that increase your cancer risk, such as genetics and environment, there are others you can control. In fact, estimates suggest that less than 30% of a person's lifetime risk of getting cancer results from uncontrollable factors. The rest you have the power to change, including your diet.
Adapting to life after cancer
Once you've completed treatment, adjusting to a "new normal" can be challenging.
Image: RuslaGuzov/ Thinkstock
Completing cancer therapy can feel like a graduation. You've done some hard work, it's paid off, and you may be ready to celebrate. But saying goodbye to treatment can arouse many of the emotions and uncertainties associated with beginning a new chapter in life.
Dr. Larissa Nekhlyudov is a general internist who works with cancer survivors at two Harvard affiliates, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. She acknowledges that cancer survivors have a lot to deal with. "Once you've had your final chemotherapy infusion or swallowed the last pill, you may find yourself facing a new set of challenges—monitoring yourself for signs of recurrence, getting recommended follow-up care, adjusting to the long-term effects of treatment, psychologically adapting to normal life, and working to stay in good health," Dr. Nekhlyudov says.
Beverage temperature tied to cancer risk
Beverages consumed at temperatures above 150° F may contribute to esophageal cancer.
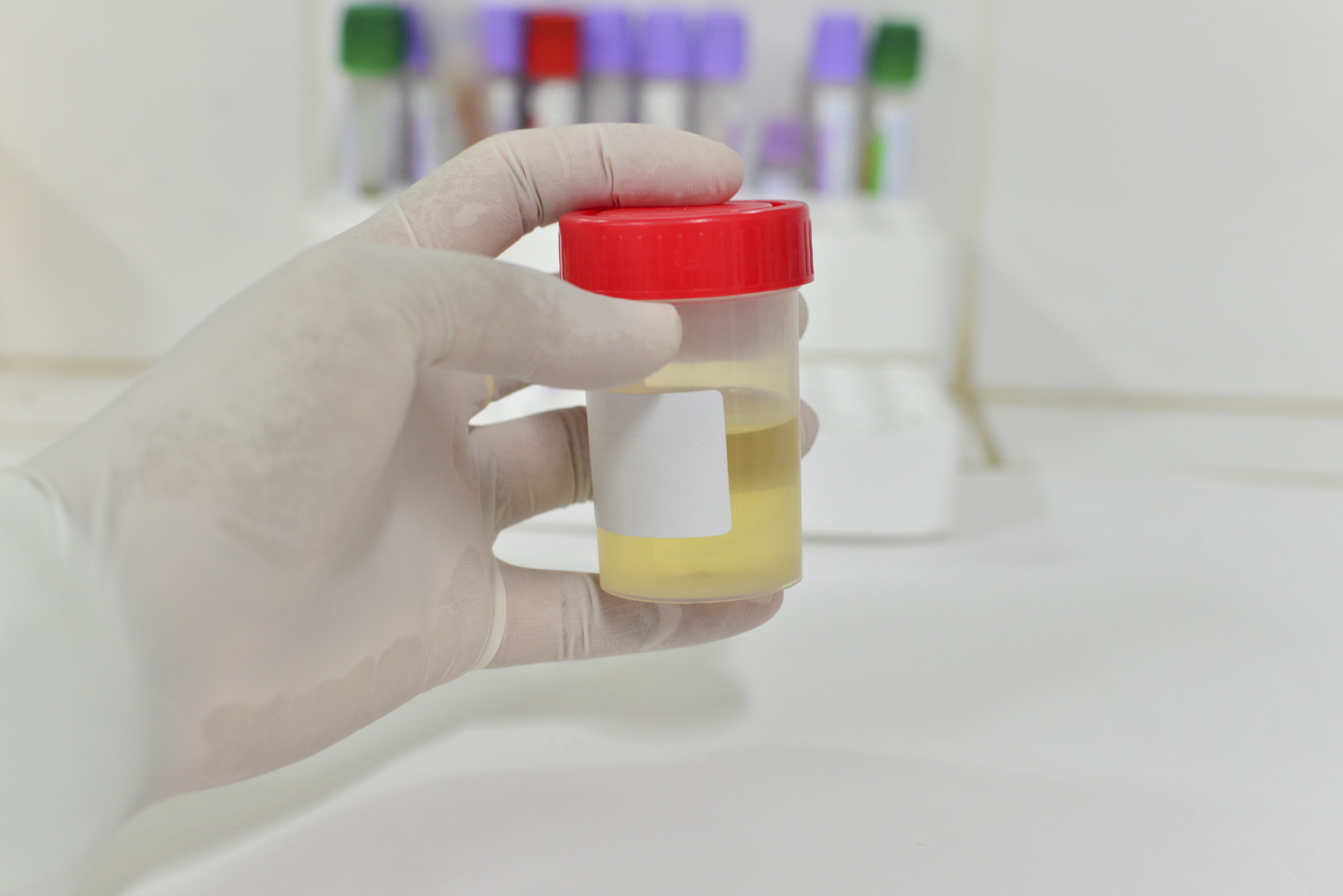
New urine test predicts high-grade prostate cancer
Researchers believe that a non-invasive screening test that can identify genetic markers for high-grade prostate cancer in urine may eventually reduce the number of prostate biopsies needed. However, experts also caution that while the number of non-invasive tests for prostate cancer diagnosis is growing, these are still early days in their development.
Gum disease may signal warning for pancreatic cancer
Research has found that people with high levels of the oral bacteria Porphyromonas gingivalis had a 59% greater risk of developing pancreatic cancer. It is too early to say whether this specific bacterium directly contributes to the disease. However, one theory is that since inflammation is related to cancer, the bacteria could cause inflammation in the pancreas. Another possibility is the bacteria are simply a marker for cancer-causing inflammation.
E-cigarettes: Good news, bad news
While e-cigarettes do not produce the tar or toxic gases found in cigarette smoke, this doesn’t make them a healthy option. The e-liquid found in e-cigarettes still contains highly addictive nicotine that also increases your risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nicotine also increases the risk of addiction to other drugs and may impair brain development. Rather than rely on the perceived benefits of e-cigarettes, people should avoid smoking altogether.
New blood test for colon cancer screening: Questions remain
In April, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a new screening test for colon cancer, making it the first blood-based test for this type of cancer. While this test does make it more convenient for people to get screened for colon cancer, it is also less exact than the current screening methods. It is important to discuss your risk factors and screening options with your doctor.
Does regular exercise reduce cancer risk?
It appears people with the highest levels of physical activity have lower rates of cancer of the esophagus, lung, kidney, colon, head and neck, rectum, bladder and breast, compared with people with the lowest levels of physical activity.

Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up