Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Allergies Archive
Articles
Is it possible for adults to develop food allergies?
Ask the doctors
��Image: © piotr_malczyk/Thinkstock
Q. Can adults develop food allergies, or is this possible only in children?
A. While food allergies are more common in children, adults can, and sometimes do, develop food allergies. You can become allergic to a food you've eaten without a problem for years, or a childhood allergy that disappeared can re-emerge. Certain foods are more likely to trigger allergic reactions than others, such as tree nuts, peanuts, shellfish, milk, and wheat.
Sniffing out sinus relief
The inflammation of chronic sinusitis can be more than just an annoyance. Here's what you can do about flare-ups.
Stuffy nose? Constant blowing? A head on the verge of exploding? Everyone battles clogged sinuses at times, and often the discomfort goes away after a few days. However, if the condition lingers or becomes more severe, you could be battling chronic sinusitis, which can affect your quality of life.
"Besides the stress of dealing with the symptoms, the condition can interfere with your sleep, lead to depression, and keep you from being active," says Dr. Ahmad R. Sedaghat, an otolaryngologist with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.
Think twice before going gluten-free
News briefs
��Image: © Elenathewise/Thinkstock
Unless you have celiac disease, banning gluten from your diet won't boost your heart health—and may actually hurt it, suggests an observational study published May 2, 2017, in The BMJ. Gluten is a protein in wheat, barley, and rye. In people with celiac disease, eating gluten triggers the body to attack the small intestine, causing inflammation and leading to malnutrition and gastrointestinal distress. The inflammation, in turn, can increase heart disease risk. In these people, eliminating gluten stops the attack on the small intestine, reduces inflammation, and helps reduce heart disease risk.
A Harvard research team wondered whether people without celiac disease might also lower their heart disease risk by eliminating gluten from their diets. In a study of more than 110,000 healthy men and women followed for about 25 years, the researchers did not find a clear difference in the number of heart attacks that occurred among people who ate the most gluten each day, compared with people who ate the least. However, in people who avoided gluten by avoiding whole grains �� which contain valuable nutrients �� the risk of heart disease rose. So, if you're among the great majority of people who don't have celiac disease, avoiding gluten won't reduce your risk of heart disease, and it might increase the risk if it means you cut back on whole grains.
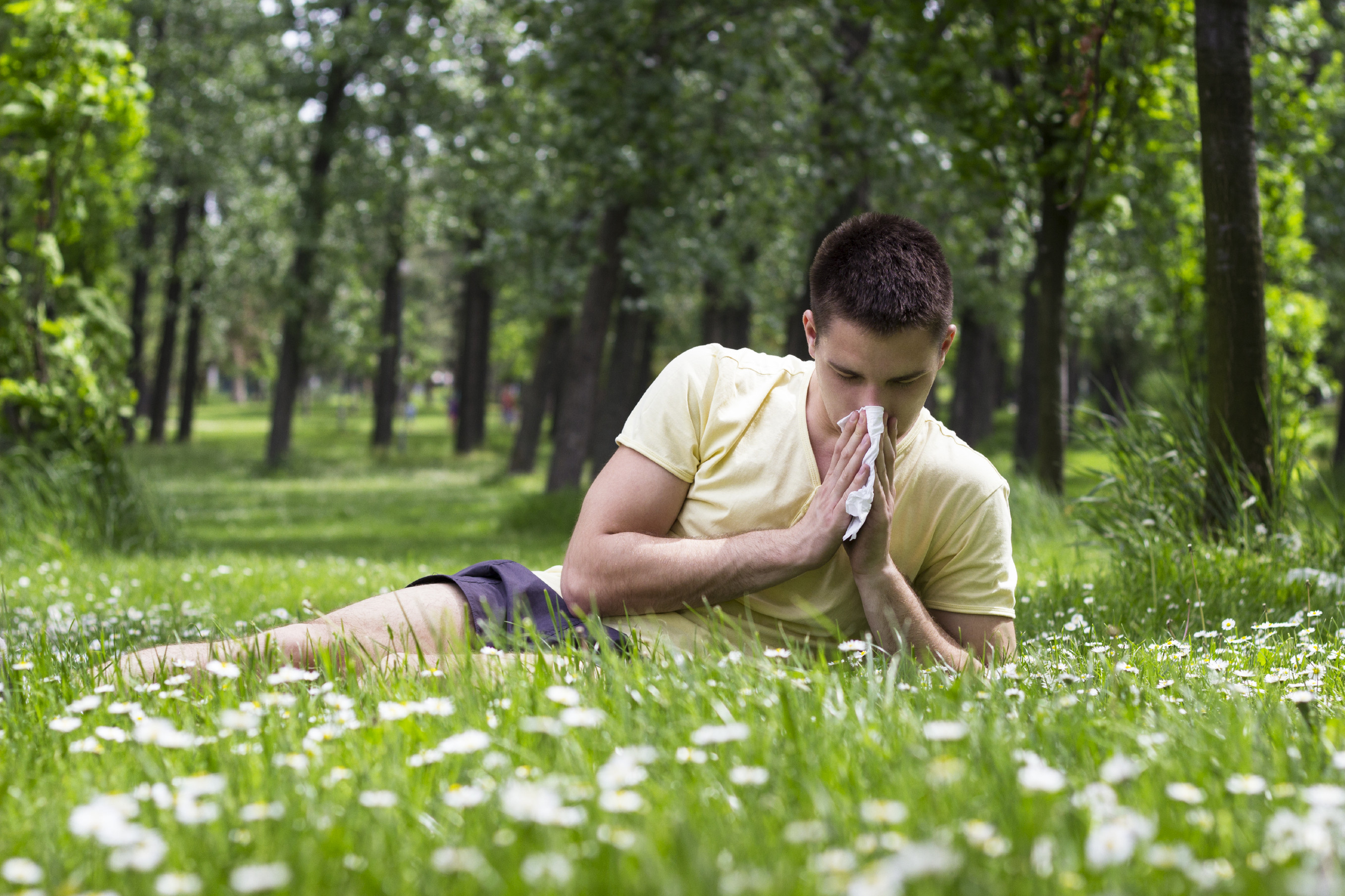
The secret to an easier allergy season
Fighting back against tiny allergens before they strike can help you avoid or reduce symptoms.
Image: iStock
The spring allergy season begins next month, and if you want to avoid symptoms, you must act now. "Pretreating allergies will lead to better control of symptoms, and maybe prevent symptoms from showing up," says Dr. Ahmad Sedaghat, an ear, nose, and throat specialist at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.
Automatic defenses
When spring allergens—typically pollen from oak, elm, birch, poplar, or maple trees, depending on where you live—float through the air and reach the nose, the body sometimes overreacts. Mast cells in the lining of the nose mistake the harmless tree particles for dangerous invaders, and summon help by releasing chemicals such as histamine and tryptase, which then recruit more immune system cells to the battle.
Dissolvable tablets don’t work for people with severe allergies to grass pollen
People with allergies to grass pollen may have cheered last year when the FDA approved a no-needles treatment —a daily tablet you dissolve under your tongue. These tables deliver low doses of grass pollen to the bloodstream. This is done to “teach” the immune system not to wage war on grass pollen. It turns out that these tablets don’t work that well. An analysis of 13 controlled clinical trials indicates that dissolvable tablets are only slightly more effective than placebos in curtailing classic symptoms of grass pollen allergy—runny nose, itchy eyes, and tickly throat. To make matters worse, more than 60% of people who used the tablets experienced irritating side effects.
3 ways to manage allergies
Allergies can cause great misery. Luckily, there are options to help manage symptoms and continue doing the things you enjoy. The goal is to find the treatment that best suits your allergies, your lifestyle, and your wallet. Here are three of the most common ways to find relief from allergy symptoms.
Antihistamines
These medications are the mainstay for treating the sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes that come with allergies. Antihistamines also relieve hives and other symptoms of some food allergies.
Many people who suffer from hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis) are familiar with the older antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton). While these drugs work well, they leave many people feeling groggy, sleepy, or just "out of it." Thankfully, the newer generation of antihistamines, including cetirizine (Zyrtec), desloratadine (Clarinex), fexofenadine (Allegra), and loratadine (Claritin), are far less likely to cause drowsiness at recommended doses. Their effects are also longer lasting, so usually you need to take them only once a day instead of every four to six hours.

Avocado nutrition: Health benefits and easy recipes

Swimming lessons save lives: What parents should know

Preventing and treating iliotibial (IT) band syndrome: Tips for pain-free movement

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up